Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM), creates objects layer by layer from digital models. Techniques include Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
Initially used mainly for rapid prototyping, recent advancements have broadened AM's scope to continuous manufacturing of end products. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the potential of AM in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where supply chain weaknesses were exposed. Developments in resin-based technologies and high-volume metal applications, especially in electro-mobility, are anticipated to open new avenues.
AM offers benefits such as on-demand production, design flexibility, faster time-to-market, improved inventory management, and superior ROI. A unique advantage is rapid prototyping, allowing quick design-to-testing transitions. AM's ability to create almost any design within its build volume enables the production of geometries not feasible with traditional methods. Furthermore, it can incorporate multiple materials into a single object, facilitating a mix of colors, textures, and mechanical properties. AM also enables mass customization, permitting the simultaneous production of multiple unique end-use parts.
Here are several personal examples of products I've manufactured using AM.
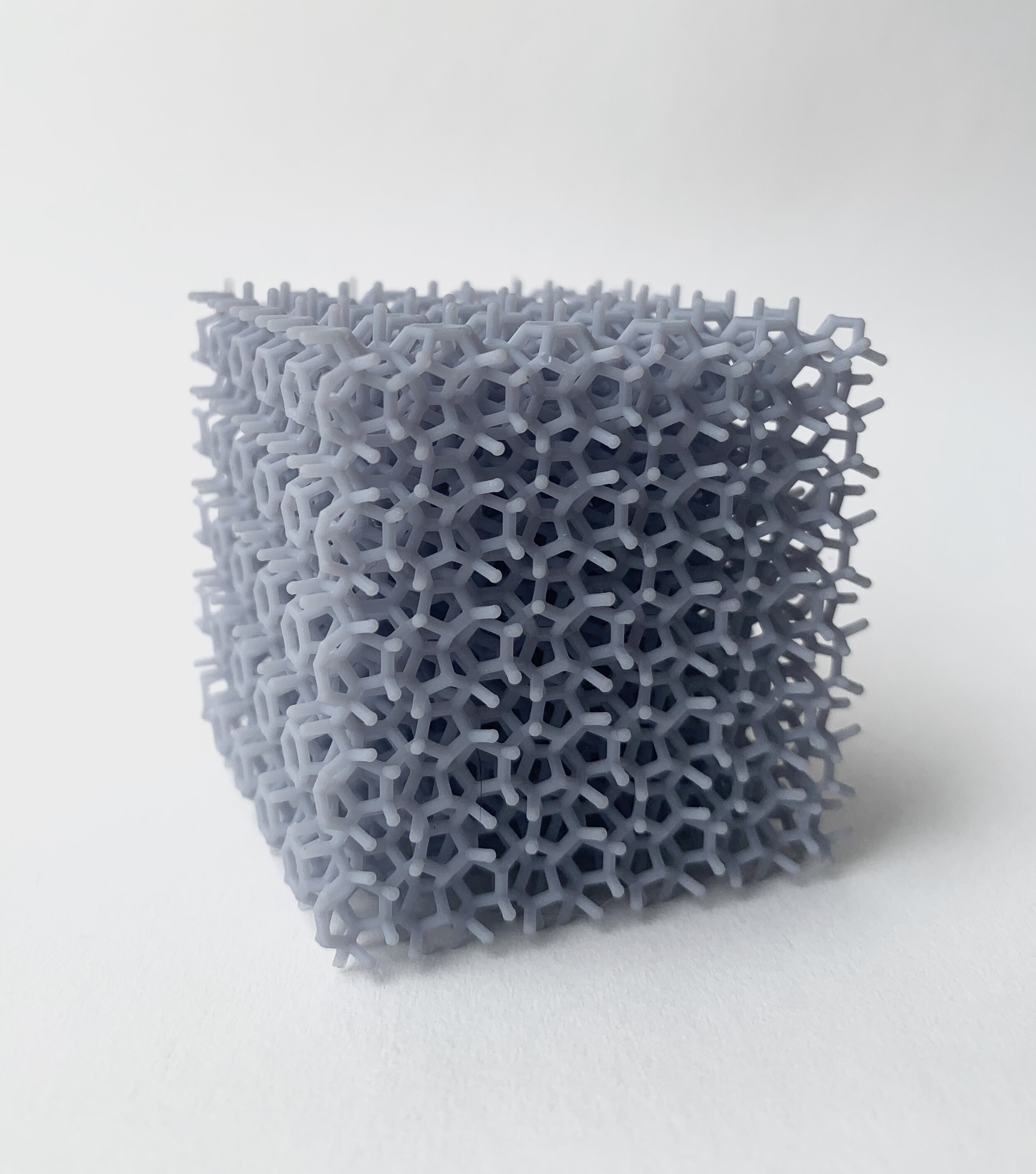
Carbone Molecule Compressible Lattice
3D Tessellation
LCD Components
FDM jig components
Star Wars Inspired Fighter FDM